Abstract
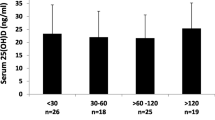
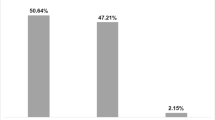
Vitamin D is an essential steroid involved in bone metabolism, cell growth, differentiation, and regulation of the minerals in the body. The main sources of this vital vitamin are adequate diet and photosynthesis in the skin. The aim of this study was to investigate the efficiency of vitamin D synthesis in 48 premenopausal women (14–44 years) in relation to three different types of dressing in summer. Women in the first group (Group I) dressed in a style which exposed the usual areas of the skin to sunlight; women in the second group (Group II wore traditional clothing with the skin of the hands and face uncovered, while the third group (Group III) dressed in traditional Islamic style, covering the whole body including hands and face. Serum 25OHD levels of Group I, Group II, and Group III were 56±41.3 nmol/l, 31.9±24.4 nmol/l, 9±5.7 nmol/l, respectively (Group I vs Group Ill, p<0.001; Group II vs Group III, p<0,03; Group I vs Group II, p>0.05). Vitamin D levels were low in 44 percent of the Group I and 60% of the Group II, which suggested that sun exposure of skin areas of hands and face may partially provide vitamin D synthesis, but may not be enough to eliminate vitamin D deficiency. All the patients in group III had vitamin D levels below normal. This study emphasizes the necessity of vitamin D fortification of food even in a sunny country where some people may not be exposed to sunlight because of inappropriate clothing or an indoor-life.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Loomis F. Skin-pigment regulation of vitamin D biosynthesis in man. Science 1967, 157: 501–506.
Reichel H., Koeffler P., Norman A.W. The role of the vitamin D endocrine system in health and disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 1989, 320: 986–991.
Holick M.F., McCollum Award lecture, 1994. Vitamin D-new horizons for the 21st century. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1994, 60: 619–630.
McLaughlin M., Fairney A., Lester E., Raggatt P.P., Brown D.J., Wills M.R. Seasonal variation in serum 25 hydroxycholecalciferol in healthy people. Lancet 1974, 11: 536–538.
Matsuoka L.Y., Ide L., Wortsman J., MacLaughlin J.A., Holick M.F. Sunscreens suppress cutaneous vitamin D3 synthesis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1987, 6: 1165–1168.
Webb Ar., Kline L., Holick J.A. Influence of season and latitude on the cutaneous synthesis of vitamin D3: Exposure to winter sunlight in Boston and Edmonton will not promote vitamin D3 synthesis in human skin. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1988, 2: 373–377.
Haddad J.G. Vitamin D- solar rays, the milky way or both. N. Engl. J. Med. 1992, 18: 1213–1215.
Goor Y., Rubinstein A. Vitamin D levels in dark- skinned people. Isr. J. Med. Sci. 1995, 31: 237–238.
Matsuoka L.Y., Wortsman J., Danneberg M.J., Hollis B.W., Lu Z., Hollis M.F. Clothing prevents ultraviolet B radiation-dependent photosynthesis of vitamin D3. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1992, 4: 1099–1103.
Sedrani S.H., Elidrissy A.W., El Arabi K.M. Sunlight and vitamin D status in Saudi subjects. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1983, 38: 129–132.
Fonseca V., Tongia R., el-Hazmi M., Abu-Aisha H. Exposure to sunlight and vitamin D deficiency in Saudi Arabian women. Postgrad. Med. J. 1984, 60: 589–591.
McKenna M. J. Differences in vitamin D status between countries in young adult and elderly. Am. J. Med. 1992, 7: 69–77.
Jacob A.I., Sallman A., Santiz S., Hollis B.W. Defective photoproduction of cholecalciferol in normal and uremic humans. J. Nutr. 1984, 114: 1313–1319.
DeHoog S. The assessment of nutritional status. In: Mahan L.K., Escott-Stump S. (Eds.), Krause’s Food, Nutrition, and Diet Therapy, ed. 9. W. B. Saunders, Philadelphia, 1996, p. 361.
Gupta M.M., Round J.M., Stamp T.C.B. Spontaneous cure of vitamin-D deficiency in Asian during summer in Britain. Lancet 1974, 14: 586–588.
Robson J., Diffey B.L. Textile and sun protection. Photodermatol. Photoimmunol. Photomed. 1990, 7: 32–34.
Groen J.J., Eshchar J., Ben-Ishay D., Alkan W.J., Ben Assa B.I. Osteomalacia among the bedouin of the Negev desert. Arch. Intern. Med. 1965, 8: 195–204.
Stamp T.C.B., Haddad T.G., Twigg C.A. Comparison of oral 25-hydroxycholecalciferol, vitamin D, and ultraviolet light as determinants of circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin D. Lancet 1977, 26: 1341–1343.
Aksnes L., Rödland O., Odegaard O.R., Bakke K.J., Aarskog D. Serum levels of vitamin D metabolites in elderly. Acta. Endocrinol. (Copenh) 1989, 121: 27–33.
Shaunak S., Ang L., Maxwell J. D. Osteomalacia presenting as a pathological fracture during pregnancy in Asian women of high social class. Br. Med. J. 1985, 16: 1215.
Weisman Y., Salama R., Harell A., Edelstein S. Serum 24,25-dihydroxyvitamin D and 25- hydroxyvitamin D concentration in femoral neck fracture. Br. Med. J. 1978, 2: 1196–1197.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alagöl, F., Shihadeh, Y., Boztepe, H. et al. Sunlight exposure and vitamin D deficiency in Turkish women. J Endocrinol Invest 23, 173–177 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03343702
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03343702