Summary.
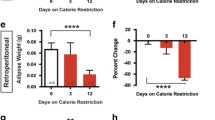
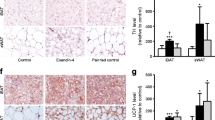
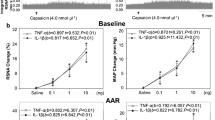
Previous studies demonstrated that angiotensin II (AngII) decreases body weight. The purpose of this study was to determine if AngII-reductions in body weight result from stimulation of sympathetic neurotransmission to interscapular brown adipose tissue (ISBAT). Following 7 days of chronic AngII infusion (350 ng/kg/min), body weight decreased compared to controls. Using superfused ISBAT tissue slices preloaded with [3H]norepinephrine (NE), evoked [3H]overflow was greater in ISBAT slices from AngII-infused rats compared to controls. When AngII was included in the buffer, evoked [3H]overflow increased in a concentration-dependent manner in ISBAT slices from AngII-infused and control rats. The EC50 for the presynaptic effect of AngII was shifted to the left in ISBAT slices from AngII-infused rats compared to controls; however, the maximal response to AngII was decreased. These results demonstrate that chronic AngII infusion enhances evoked release of NE from ISBAT sympathetic nerve terminals. Moreover, responsiveness to the presynaptic effect of AngII was altered following chronic AngII infusion. Increased sympathetic neurotransmission to ISBAT may contribute to AngII-regulation of body weight.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received December 28, 1998; accepted February 10, 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
English, V., Cassis, L. Facilitation of sympathetic neurotransmission contributes to angiotensin regulation of body weight. J Neural Transm 106, 631–644 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s007020050185
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s007020050185